Advanced audiovisual systems can introduce technical challenges involving hardware compatibility, network security and bandwidth management. Having online meetings repeatedly fail due to seemingly simple glitches like connectivity drops or echoes can be frustrating. However, the hidden cost of downtime can lead to even more of a headache.
An AV integrator bridges the gap between your facilities and your IT team by transforming disjointed hardware into a unified, secure ecosystem. Learn what an AV integrator does and why you should bring one on board.
What Is an AV Integrator?
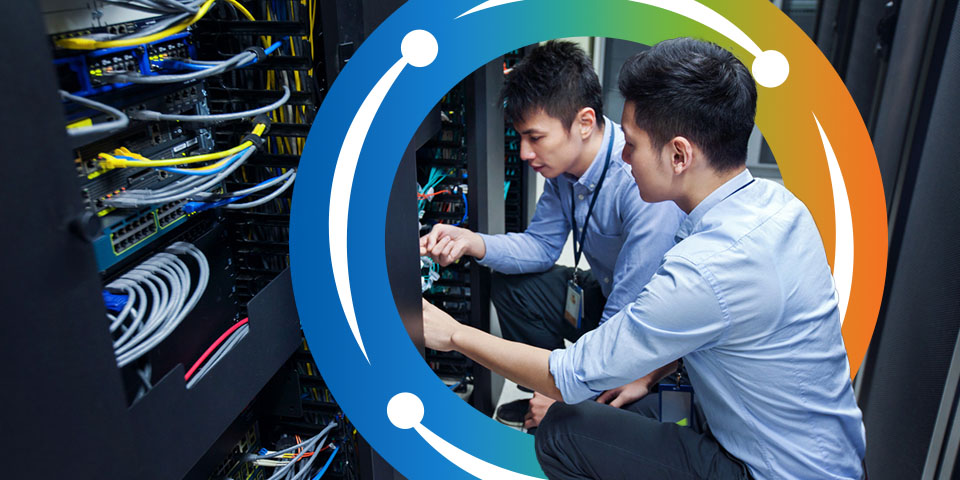
An AV integrator is a specialist who helps you design, install and maintain your audiovisual technologies. They blend each disparate piece of hardware, such as cameras, microphones, displays and control panels, into a single, user-friendly ecosystem that enhances communication and collaboration efficiency.
AV integrators are not one-time hardware sellers and installers with a transactional relationship. Instead, they’ll manage your technology from the initial planning and design through optimizing and end-of-life planning. It’s a strategic, ongoing responsibility to ensure every component of your AV system performs seamlessly from the moment you press the start button.
Signs You Need a Professional AV Integration Partner
How can you determine when it’s time to hire a professional for your AV integration?
1. You Have Complex Network Needs
AV systems and technology constantly evolve. Compared to simpler setups with “plug-and-play” hardware, they are now more sophisticated, network-dependent applications that need advanced IT techniques to work properly. Such is the case with the industry shift to AV-over-IP.
You should also consider your network security and segmentation, cross-platform compatibility, bandwidth and latency management. You can’t DIY these requirements. You need an expert to manage latency and prevent heavy data packets from crashing your email server.
2. You Need to Provide Hybrid Equity
If your company has shifted into a hybrid work environment, you may need an AV integrator to create equity between your on-site and remote teams. Otherwise, employees who work off-site may feel their contributions are less welcome and valuable than those who choose to be in the office.
An AV integrator can address this challenge by transforming static online meeting rooms into dynamic spaces that promote collaboration. Pros calibrate advanced tech and tools like 360-degree cameras, active speaker tracking, intelligent microphones and digital whiteboards to give everyone a voice, regardless of their location.
3. Regulatory Compliance Is Nonnegotiable
Upgrading your AV technology requires adhering to strict privacy rules with each connected component. In addition to blanket legal and safety regulations, there are also industry-specific standards, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. An integrator can make all your recording devices and wireless transmission gateways fulfill with these stringent requirements.
4. You Are Scaling
Your technology will become increasingly complex as your business grows and you depend less on in-house solutions. An AV integrator will ensure your technology stays efficient and scalable if you add new locations, build larger rooms or expand to hybrid work capabilities.
Of course, a professional’s detailed technical knowledge and experience will also benefit your overworked in-house IT team.
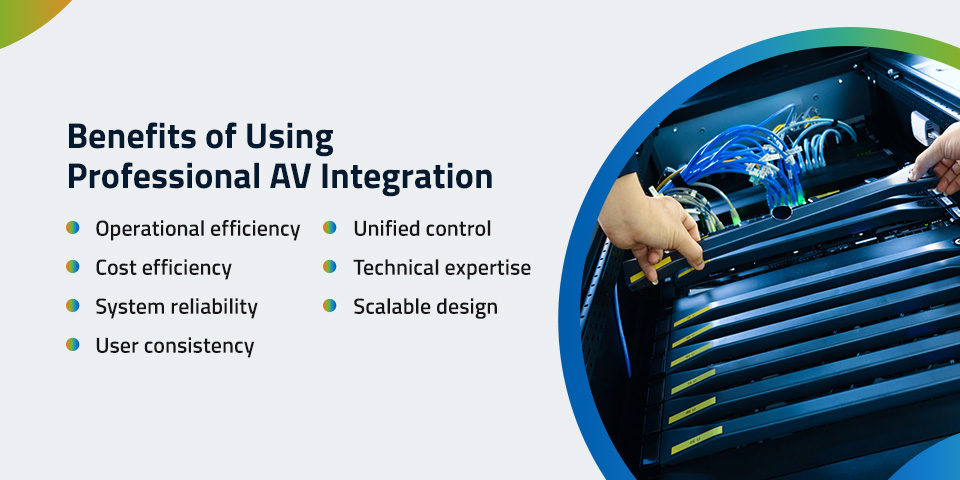
Benefits of Using Professional AV Integration
An AV integrator can become a valued team member who keeps communications flowing smoothly.
- Operational efficiency: Professional integration makes your AV system work seamlessly, with little friction between technologies and daily operations.
- Cost efficiency: When you have a thoughtfully designed AV system, it’s less likely to cause trouble or stop working unexpectedly. A reputable third party can save you time and money.
- System reliability: Proper installation and maintenance ensure the system performs smoothly and consistently.
- User consistency: A well-integrated AV system will have an intuitive interface with less of a learning curve for personnel.
- Unified control: With each AV component working in unison, you’ll have centralized management at your fingertips, letting you oversee multiple environments.
- Technical expertise: Integrators bring a depth of technical know-how and industry insight that your internal team might lack.
- Scalable design: An AV integrator builds your system with growth in mind. You can rest assured that your system will not need frequent, expensive upgrades to keep up.
AV Integration Workflow
An AV integrator oversees the installation and management of your AV solutions and integrates them for maximum efficiency and productivity. Their responsibilities combine technical engineering and project management with a focus on user-friendly design.
Here’s what an AV integrator’s typical workflow involves.
- Needs analysis: Each project starts with a better understanding of your goals and ideal AV setup. They’ll check your space’s acoustics, lighting and sight lines to determine what gear you need, preventing you from wasting money.
- System engineering: Using the information from the needs analysis, they create detailed blueprints. An engineer draws a diagram to show how the AV equipment connects to the network, which eliminates surprise incompatibility issues.
- Equipment sourcing: Once you approve the design, the integrator will start purchasing specific equipment from authorized distributors and verify that all hardware is compatible.
- System installation: Typically, they’ll build and wire the equipment racks at their facility before transporting the system to your site for installation. This arrangement minimizes disruptions to your daily operations.
- Network calibration: AV integrators will configure the network settings, including setting up virtual local area networks to separate AV traffic from data traffic and configuring quality of service to prioritize voice data so calls don’t drop.
- System testing: The AV integrator will run through a rigorous checklist to ensure each component responds instantly and as it should. They’ll also simulate failures to see if the system successfully recovers automatically.
- Managed support: Finally, the integrator will transition into a life cycle manager role to provide proactive, ongoing support after the installation.
What to Look for in an AV Partner
Choosing an AV partner requires more than a detailed pricing comparison. You want a team that understands your goals, workflow and environment, because the relationship should last well beyond installation.
Look for qualities like these.
- Personalized solutions: – Every project is different. Choose a partner who can tailor systems to your specific challenges rather than relying on one‑size‑fits‑all designs.
- Scalable approach: A future‑ready partner designs solutions that grow with your organization and adapt to new technologies.
- Service‑level agreements: Comprehensive SLAs demonstrate a commitment to system reliability and outline clear, cost‑effective support options.
- Unified capabilities: The best partners manage hardware and networking. Selecting a vendor that only handles one side can create gaps in performance and accountability.
- Vendor certifications: Credentials from leading manufacturers show that the team has completed rigorous technical training and brings proven expertise to your project.
Partner With Morefield for Seamless Integration
An AV system is the heart of your daily operations, especially if your company has a hybrid work environment. Since every minute you spend troubleshooting eats away at your productivity and credibility, you can’t DIY your communication and collaboration tools.
Morefield is a technology solutions company that offers integrated AV communication technology systems and services. In our over 70 years of experience, clients across various sectors have trusted us to provide expert AV installations and support.
Connect with us online for further information.